| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-05-27 01:19:10 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:22:26 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM041270 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | PGP(16:0/18:1(11Z)) |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
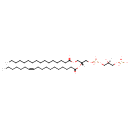
| Description | PGP(16:0/18:1(11Z)) is a phosphatidylglycerolphosphate or glycerophospholipid (PGP or GP). It is a glycerophospholipid in which a phosphoglycerol moiety occupies a glycerol substitution site followed by another phosphate moiety. As is the case with diacylglycerols, phosphatidylglycerols can have many different combinations of fatty acids of varying lengths and saturation attached at the C-1 and C-2 positions. Fatty acids containing 16, 18 and 20 carbons are the most common. PGP(16:0/18:1(11Z)), in particular, consists of one chain of palmitic acid at the C-1 position and one chain of vaccenic acid at the C-2 position. The palmitic acid moiety is derived from fish oils, milk fats, vegetable oils and animal fats, while the vaccenic acid moiety is derived from butter fat and animal fat. Phosphatidylglycerolphosphate is present at a level of 1-2% in most animal tissues, but it can be the second most abundant phospholipid in lung surfactant at up to 11% of the total. It is well established that the concentration of Phosphatidylglycerolphosphate increases during fetal development. Phosphatidylglycerolphosphate may be present in animal tissues merely as a precursor for diphosphatidylglycerol (cardiolipin). Phosphatidylglycerol is formed from phosphatidic acid by a sequence of enzymatic reactions that proceeds via the intermediate, cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CDP-diacylglycerol). Bioynthesis proceeds by condensation of phosphatidic acid and cytidine triphosphate with elimination of pyrophosphate via the action of phosphatidate cytidyltransferase (or CDP-synthase). CDP-diacylglycerol then reacts with glycerol-3-phosphate via phosphatidylglycerophosphate synthase to form 3-sn-phosphatidyl-1'-sn-glycerol 3'-phosphoric acid, with the release of cytidine monophosphate (CMP). Finally, phosphatidylglycerol is formed by the action of specific phosphatases.
While most phospholipids have a saturated fatty acid on C-1 and an unsaturated fatty acid on C-2 of the glycerol backbone, the fatty acid distribution at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol within phospholipids is continually in flux, owing to phospholipid degradation and the continuous phospholipid remodeling that occurs while these molecules are in membranes. PGPs have a net charge of -1 at physiological pH and are found in high concentration in mitochondrial membranes and as components of pulmonary surfactant. PGP also serves as a precursor for the synthesis of cardiolipin. PGP is synthesized from CDP-diacylglycerol and glycerol-3-phosphate. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | |
|---|
| Contaminant Type | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 1-Palmitoyl-2-vaccenoyl-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1'-sn-glycerol-3'-phosphate) | HMDB | | 3-sn-Phosphatidyl-1'-sn-glycerol 3'-phosphoric acid | HMDB | | PGP(16:0/18:1) | HMDB | | PGP(16:0/18:1n7) | HMDB | | PGP(16:0/18:1W7) | HMDB | | PGP(34:1) | HMDB | | 1-Hexadecanoyl-2-(11Z-octadecenoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phospho-(1'-sn-glycerol-3'-phosphate) | HMDB | | PGP(16:0/18:1(11Z)) | Lipid Annotator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C40H78O13P2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 828.999 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 828.492 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | [(2S)-3-({[(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy](hydroxy)phosphoryl}oxy)-2-hydroxypropoxy]phosphonic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | (2S)-3-{[(2R)-3-(hexadecanoyloxy)-2-[(11Z)-octadec-11-enoyloxy]propoxy(hydroxy)phosphoryl]oxy}-2-hydroxypropoxyphosphonic acid |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@](O)(COP(O)(O)=O)COP(O)(=O)OC[C@@]([H])(COC(=O)CCCCCCCCCCCCCCC)OC(=O)CCCCCCCCC\C=C/CCCCCC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C40H78O13P2/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-18-20-22-24-26-28-30-32-40(43)53-38(36-52-55(47,48)51-34-37(41)33-50-54(44,45)46)35-49-39(42)31-29-27-25-23-21-19-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2/h13,15,37-38,41H,3-12,14,16-36H2,1-2H3,(H,47,48)(H2,44,45,46)/b15-13-/t37-,38+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | BMNRKKFJIDDAOJ-GPJPVTGXSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as phosphatidylglycerophosphates. These are glycerophosphoglycerophosphates in which two fatty acids are bonded to the 1-glycerol moiety through ester linkages. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Glycerophospholipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Glycerophosphoglycerophosphates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Phosphatidylglycerophosphates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Diacylglycerophosphoglycerophosphate
- Sn-glycerol-3-phosphate
- Fatty acid ester
- Monoalkyl phosphate
- Dialkyl phosphate
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic phosphoric acid derivative
- Phosphoric acid ester
- Alkyl phosphate
- Fatty acyl
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Appearance | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-07gs-0290050140-148fec6eb4e24653d8cb | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0ap1-1391021010-efd28ea9fb049e8d7665 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0cdr-3693120100-4fdd0f0ad588f3b3e14f | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-057r-2090020010-b11d66a904bbae3ec6b7 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-004i-9060000000-40e0bb1c56654c979770 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004i-9010000000-aff4a02985fce2b7bf17 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-2100060690-32bb83a9b1be9f764a2d | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0560-5700069600-27f97883562b1ae9b803 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0zfs-5473910000-f55edef154f852be162f | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0010000090-7f4e07b96246f1c72f89 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0fb9-2090040040-18bedf9abdee3a8df0cb | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0fba-3092051000-8b66f3689b7055103bda | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0013475 |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB029475 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 7826086 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 9547136 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | YMDB14376 |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | |
|---|