Methylglutarylcarnitine (CHEM041118)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2016-05-27 01:14:42 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:22:24 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | CHEM041118 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Methylglutarylcarnitine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Methylmalonylcarnitine belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acyl carnitines. These are organic compounds containing a fatty acid with the carboxylic acid attached to carnitine through an ester bond. Thus, methylmalonylcarnitine is considered to be a fatty ester lipid molecule. Methylmalonylcarnitine is a very hydrophobic molecule, practically insoluble (in water), and relatively neutral. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contaminant Sources |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contaminant Type | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
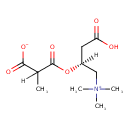
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C11H19NO6 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 261.272 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 261.121 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 3-{[(2S)-1-carboxy-3-(trimethylazaniumyl)propan-2-yl]oxy}-2-methyl-3-oxopropanoate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 3-{[(2S)-1-carboxy-3-(trimethylammonio)propan-2-yl]oxy}-2-methyl-3-oxopropanoate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CC(C(O)=O)C(=O)O[C@@H](CC([O-])=O)C[N+](C)(C)C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C11H19NO6/c1-7(10(15)16)11(17)18-8(5-9(13)14)6-12(2,3)4/h7-8H,5-6H2,1-4H3,(H-,13,14,15,16)/t7?,8-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | XROYFEWIXXCPAW-MQWKRIRWSA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acyl carnitines. These are organic compounds containing a fatty acid with the carboxylic acid attached to carnitine through an ester bond. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Fatty Acyls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Fatty acid esters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Acyl carnitines | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0013133 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB029306 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 53481699 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ECMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||