Valerylcarnitine (CHEM041113)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2016-05-27 01:14:37 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:22:24 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | CHEM041113 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Valerylcarnitine | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Valerylcarnitine, also known as pentanoylcarnitine or C5-carnitine, belongs to the class of organic compounds known as fatty acid esters. These are carboxylic ester derivatives of a fatty acid. Valerylcarnitine is possibly soluble (in water) and an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Valerylcarnitine has been found to be associated with several diseases known as short/branched chain acyl-coa dehydrogenase deficiency, pregnancy, obesity, and eosinophilic esophagitis; also valerylcarnitine has been linked to the inborn metabolic disorders including isovaleric acidemia. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contaminant Sources |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contaminant Type | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
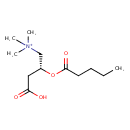
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C12H23NO4 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 245.315 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 245.163 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | [(2R)-3-carboxy-2-(pentanoyloxy)propyl]trimethylazanium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | [(2R)-3-carboxy-2-(pentanoyloxy)propyl]trimethylazanium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | CCCCC(=O)O[C@@H](CC([O-])=O)C[N+](C)(C)C | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C12H23NO4/c1-5-6-7-12(16)17-10(8-11(14)15)9-13(2,3)4/h10H,5-9H2,1-4H3/t10-/m0/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | VSNFQQXVMPSASB-JTQLQIEISA-N | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as fatty acid esters. These are carboxylic ester derivatives of a fatty acid. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Fatty Acyls | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Fatty acid esters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Fatty acid esters | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0013128 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB029301 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 17353685 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 85095 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 10157322 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ECMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||