| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-05-27 01:11:24 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:22:23 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM041082 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Prostaglandin H1 |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Prostaglandin H1 (PGH1) is the precursor to all 1-series thromboxanes, and is a suicide inhibitor of platelet thromboxane synthase, possessing a Ki of 28 mM.2 PGH1 also acts on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) by stimulating AhR transformation and DNA binding in vitro. It also induces AhR-dependent reporter gene expression in mouse hepatoma cells in culture.3. Prostaglandins are eicosanoids. The eicosanoids consist of the prostaglandins (PGs), thromboxanes (TXs), leukotrienes (LTs), and lipoxins (LXs). The PGs and TXs are collectively identified as prostanoids. Prostaglandins were originally shown to be synthesized in the prostate gland, thromboxanes from platelets (thrombocytes), and leukotrienes from leukocytes, hence the derivation of their names. All mammalian cells except erythrocytes synthesize eicosanoids. These molecules are extremely potent, able to cause profound physiological effects at very dilute concentrations. All eicosanoids function locally at the site of synthesis, through receptor-mediated G-protein linked signalling pathways. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | |
|---|
| Contaminant Type | Not Available |
|---|
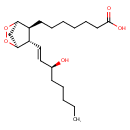
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 9alpha,11alpha-Epidioxy-15(S)-hydroxy-13-trans-prostenoate | HMDB | | 9alpha,11alpha-Epidioxy-15(S)-hydroxy-13-trans-prostenoic acid | HMDB | | PGH(,1) | HMDB | | 7-[(1S,4R,5S,6S)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-Hydroxyoct-1-en-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-5-yl]heptanoate | Generator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C20H34O5 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 354.481 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 354.241 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 7-[(1S,4R,5S,6S)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-en-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-5-yl]heptanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 7-[(1S,4R,5S,6S)-6-[(1E,3S)-3-hydroxyoct-1-en-1-yl]-2,3-dioxabicyclo[2.2.1]heptan-5-yl]heptanoic acid |
|---|
| SMILES | CCCCC[C@H](O)\C=C\[C@@H]1[C@@H]2C[C@@H](OO2)[C@H]1CCCCCCC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C20H34O5/c1-2-3-6-9-15(21)12-13-17-16(18-14-19(17)25-24-18)10-7-4-5-8-11-20(22)23/h12-13,15-19,21H,2-11,14H2,1H3,(H,22,23)/b13-12+/t15-,16-,17-,18+,19-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | NTAYABHEVAQSJS-NDWDMBLISA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as prostaglandins and related compounds. These are unsaturated carboxylic acids consisting of a 20 carbon skeleton that also contains a five member ring, and are based upon the fatty acid arachidonic acid. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Fatty Acyls |
|---|
| Sub Class | Eicosanoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Prostaglandins and related compounds |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Prostaglandin skeleton
- Long-chain fatty acid
- Fatty alcohol
- Heterocyclic fatty acid
- Hydroxy fatty acid
- Ortho-dioxane
- Ortho-dioxolane
- Dialkyl peroxide
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid
- Oxacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organic oxide
- Organic oxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Appearance | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-01wu-4192000000-bc99d7562ca1dd0e54a9 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (2 TMS) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-00gr-9242300000-88d88d034143c85f0ad0 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-000i-0019000000-2c081e879b4aa402d298 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-05n0-5579000000-590ab4244e220b0caa9f | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-05to-9300000000-f6e1bf96abe81b6952fc | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0009000000-142292a24df2444e493e | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0f79-1029000000-18da725097025f2b15f8 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9242000000-15942f2140f731ead6d9 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014r-0009000000-9366db7527d16336dec2 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-014l-5379000000-eeaefff600dc9037681a | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-05mo-9500000000-5251e610b43b3ef3ae45 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udi-0009000000-c17a630eaa2ea7e31c4e | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00di-0009000000-17100385a9b3f576ce83 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0f83-2095000000-077e73dd859c29e303ec | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0013041 |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB029266 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 30776687 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 50921242 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | |
|---|