Chondroitin 4-sulfate (CHEM034928)
| Record Information | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Version | 1.0 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Creation Date | 2016-05-26 05:20:31 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:21:13 UTC | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accession Number | CHEM034928 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Identification | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Name | Chondroitin 4-sulfate | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Small Molecule | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | Chondroitin 4-sulfate belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. Chondroitin 4-sulfate is possibly soluble (in water) and an extremely weak basic (essentially neutral) compound (based on its pKa). Adenosine 3',5'-diphosphate and chondroitin 4-sulfate can be biosynthesized from phosphoadenosine phosphosulfate and chondroitin through the action of the enzyme carbohydrate sulfotransferase 11. In cattle, chondroitin 4-sulfate is involved in the metabolic pathway called the sulfate/sulfite metabolism pathway. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contaminant Sources |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Contaminant Type | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
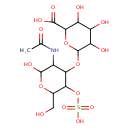
| Chemical Structure | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synonyms |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Formula | C70H97N5O71S5 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Molecular Mass | 2304.835 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Monoisotopic Mass | 2303.274 g/mol | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| IUPAC Name | 6-{[3-acetamido-2-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-5-(sulfooxy)oxan-4-yl]oxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Traditional Name | 6-{[3-acetamido-2-hydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-5-(sulfooxy)oxan-4-yl]oxy}-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(O)O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@]([H])(OS([O-])(=O)=O)[C@]([H])(O[C@]2([H])O[C@]([H])(C([O-])=O)[C@@]([H])(O[C@]3([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@]([H])(OS([O-])(=O)=O)[C@]([H])(O[C@]4([H])O[C@]([H])(C([O-])=O)[C@@]([H])(O[C@]5([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@]([H])(OS([O-])(=O)=O)[C@]([H])(O[C@]6([H])O[C@]([H])(C([O-])=O)[C@@]([H])(O[C@]7([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@]([H])(OS([O-])(=O)=O)[C@]([H])(O[C@]8([H])O[C@]([H])(C([O-])=O)[C@@]([H])(O[C@]9([H])O[C@]([H])(CO)[C@]([H])(OS([O-])(=O)=O)[C@]([H])(O[C@]%10([H])O[C@]([H])(C([O-])=O)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]%10([H])O)[C@@]9([H])NC(C)=O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]8([H])O)[C@@]7([H])NC(C)=O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]6([H])O)[C@@]5([H])NC(C)=O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]4([H])O)[C@@]3([H])NC(C)=O)[C@]([H])(O)[C@@]2([H])O)[C@@]1([H])NC(C)=O | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C70H107N5O71S5/c1-11(81)71-21-42(37(142-147(108,109)110)16(6-76)123-61(21)107)128-67-33(93)28(88)47(52(138-67)57(99)100)133-63-23(73-13(3)83)44(39(18(8-78)125-63)144-149(114,115)116)130-69-35(95)30(90)49(54(140-69)59(103)104)135-65-25(75-15(5)85)46(41(20(10-80)127-65)146-151(120,121)122)132-70-36(96)31(91)50(55(141-70)60(105)106)136-64-24(74-14(4)84)45(40(19(9-79)126-64)145-150(117,118)119)131-68-34(94)29(89)48(53(139-68)58(101)102)134-62-22(72-12(2)82)43(38(17(7-77)124-62)143-148(111,112)113)129-66-32(92)26(86)27(87)51(137-66)56(97)98/h16-55,61-70,76-80,86-96,107H,6-10H2,1-5H3,(H,71,81)(H,72,82)(H,73,83)(H,74,84)(H,75,85)(H,97,98)(H,99,100)(H,101,102)(H,103,104)(H,105,106)(H,108,109,110)(H,111,112,113)(H,114,115,116)(H,117,118,119)(H,120,121,122)/p-10/t16-,17-,18-,19-,20-,21-,22-,23-,24-,25-,26+,27+,28-,29-,30-,31-,32-,33-,34-,35-,36-,37+,38+,39+,40+,41+,42-,43-,44-,45-,46-,47+,48+,49+,50+,51+,52+,53+,54+,55+,61-,62+,63+,64+,65+,66-,67-,68-,69-,70-/m1/s1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| InChI Key | PNOCSDIJELBTOO-BHQNPOKRSA-D | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Taxonomy | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as acylaminosugars. These are organic compounds containing a sugar linked to a chain through N-acyl group. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kingdom | Organic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Super Class | Organic oxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Class | Organooxygen compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sub Class | Carbohydrates and carbohydrate conjugates | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Direct Parent | Acylaminosugars | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Alternative Parents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Substituents |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteromonocyclic compounds | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Descriptors | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Origin | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cellular Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tissue Locations | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pathways | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Applications | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Biological Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Roles | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Physical Properties | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| State | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Appearance | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Experimental Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Predicted Properties |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Spectra |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Profile | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Route of Exposure | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metabolism | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicity Values | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Lethal Dose | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Uses/Sources | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Health Effects | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Symptoms | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treatment | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Concentrations | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Not Available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External Links | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| DrugBank ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| HMDB ID | HMDB0000652 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| FooDB ID | FDB022163 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BiGG ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| BioCyc ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| METLIN ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemspider ID | 3570966 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ChEBI ID | 37397 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| PubChem Compound ID | 4368136 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Kegg Compound ID | C00634 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| YMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ECMDB ID | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| MSDS | Not Available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General References | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||