| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-05-26 00:47:06 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:18:47 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM028903 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Stevioside |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Constituent of Stevia rebaudiana (stevia). Sweetening agent which is 300 times sweeter than sucrose. Stevia rebaudiana is extensively cultivated in Japan, and Stevioside is a permitted sweetener in that country
Rebaudioside B, D, and E may also be present in minute quantities; however, it is suspected that rebaudioside B is a byproduct of the isolation technique. The two majority compounds stevioside and rebaudioside, primarily responsible for the sweet taste of stevia leaves, were first isolated by two French chemists in 1931. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | |
|---|
| Contaminant Type | Not Available |
|---|
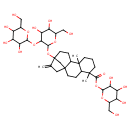
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Diterpene glycoside | HMDB | | Eupatorin? | HMDB | | Rebaudin | HMDB | | Stevin? | HMDB | | Steviosin | HMDB | | 3,4,5-Trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl 13-{[4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-{[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]oxy}-5,9-dimethyl-14-methylidenetetracyclo[11.2.1.0¹,¹⁰.0⁴,⁹]hexadecane-5-carboxylic acid | Generator | | Stevioside | MeSH | | Steviol glycoside | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C38H60O18 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 804.872 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 804.378 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 57817-89-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl 13-{[4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-{[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}oxan-2-yl]oxy}-5,9-dimethyl-14-methylidenetetracyclo[11.2.1.0¹,¹⁰.0⁴,⁹]hexadecane-5-carboxylate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | stevioside |
|---|
| SMILES | CC12CCCC(C)(C1CCC13CC(=C)C(C1)(CCC23)OC1OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C1OC1OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C1O)C(=O)OC1OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C38H60O18/c1-16-11-37-9-5-20-35(2,7-4-8-36(20,3)34(50)55-32-29(49)26(46)23(43)18(13-40)52-32)21(37)6-10-38(16,15-37)56-33-30(27(47)24(44)19(14-41)53-33)54-31-28(48)25(45)22(42)17(12-39)51-31/h17-33,39-49H,1,4-15H2,2-3H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | UEDUENGHJMELGK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as steviol glycosides. These are prenol lipids containing a carbohydrate moiety glycosidically linked to a steviol (a diterpenoid based on a 13-Hydroxykaur-16-en-18-oic acid) moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Terpene glycosides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Steviol glycosides |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Steviol glycoside
- Diterpenoid
- Kaurane diterpenoid
- Fatty acyl glycoside
- Fatty acyl glycoside of mono- or disaccharide
- Disaccharide
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- Oxane
- Fatty acyl
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Polyol
- Oxacycle
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Acetal
- Primary alcohol
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Alcohol
- Carbonyl group
- Organooxygen compound
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Appearance | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-01tc-0103809210-618c8917bf91bf14e0da | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-040r-0104904000-6810fe906f79bdcb23c6 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-02w9-0415902100-c4cc22c8df7fa9e745e6 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0fic-1402569430-00c6ad06eb887c4431b8 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-01t9-1911715300-ccd331e4189584049205 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004i-4901410000-d567568eafd4a9c77616 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0034945 |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB013538 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00003485 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Stevioside |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 477115 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 548198 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | C09189 |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | |
|---|