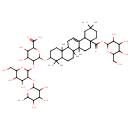| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-05-25 23:34:04 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:18:24 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM027199 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Lablaboside A |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Lablaboside A is found in pulses. Lablaboside A is a constituent of hyacinth bean seeds (Dolichos lablab). |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | |
|---|
| Contaminant Type | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 3-O-(alpha-L-Rhamnopyranosyl (1-2)-beta-D-galactopyranosyl (1-2)-beta-D-glucopyranosiduronic acid)-28-O-(beta-D-glucopyranosyl) oleanolic acid | HMDB | | 6-{[4,4,6a,6b,11,11,14b-heptamethyl-8a-({[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}carbonyl)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a,14,14a,14b-icosahydropicen-3-yl]oxy}-5-{[4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy]oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,4-dihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylate | HMDB | | Lablaboside a | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C54H86O23 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 1103.247 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 1102.556 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 209802-26-6 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 6-{[4,4,6a,6b,11,11,14b-heptamethyl-8a-({[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}carbonyl)-1,2,3,4,4a,5,6,6a,6b,7,8,8a,9,10,11,12,12a,14,14a,14b-icosahydropicen-3-yl]oxy}-5-{[4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy]oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,4-dihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | 6-{[4,4,6a,6b,11,11,14b-heptamethyl-8a-({[3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxy}carbonyl)-1,2,3,4a,5,6,7,8,9,10,12,12a,14,14a-tetradecahydropicen-3-yl]oxy}-5-{[4,5-dihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)-3-[(3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyloxan-2-yl)oxy]oxan-2-yl]oxy}-3,4-dihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid |
|---|
| SMILES | CC1OC(OC2C(O)C(O)C(CO)OC2OC2C(O)C(O)C(OC2OC2CCC3(C)C(CCC4(C)C3CC=C3C5CC(C)(C)CCC5(CCC43C)C(=O)OC3OC(CO)C(O)C(O)C3O)C2(C)C)C(O)=O)C(O)C(O)C1O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C54H86O23/c1-22-30(57)33(60)38(65)44(70-22)75-41-35(62)32(59)26(21-56)72-46(41)76-42-37(64)36(63)40(43(67)68)74-47(42)73-29-12-13-51(6)27(50(29,4)5)11-14-53(8)28(51)10-9-23-24-19-49(2,3)15-17-54(24,18-16-52(23,53)7)48(69)77-45-39(66)34(61)31(58)25(20-55)71-45/h9,22,24-42,44-47,55-66H,10-21H2,1-8H3,(H,67,68) |
|---|
| InChI Key | VLPIKCMVDFDYQR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as triterpene saponins. These are glycosylated derivatives of triterpene sapogenins. The sapogenin moiety backbone is usually based on the oleanane, ursane, taraxastane, bauerane, lanostane, lupeol, lupane, dammarane, cycloartane, friedelane, hopane, 9b,19-cyclo-lanostane, cycloartane, or cycloartanol skeleton. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Terpene glycosides |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Triterpene saponins |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Triterpene saponin
- Triterpenoid
- Oligosaccharide
- Fatty acyl glycoside
- 1-o-glucuronide
- O-glucuronide
- Glucuronic acid or derivatives
- Glycosyl compound
- O-glycosyl compound
- Beta-hydroxy acid
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Fatty acyl
- Hydroxy acid
- Pyran
- Oxane
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Secondary alcohol
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Oxacycle
- Carboxylic acid
- Acetal
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Polyol
- Primary alcohol
- Alcohol
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Appearance | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0j7r-6902013347-155eb70c316345ff5336 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-03gi-6902113311-97cd8df6df0358e75a01 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-03fr-5901002200-abc01af23e612f639df0 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0udr-7900000105-90fa4b9e27f7084465eb | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9301000206-78ad9fbb9e60db7a015e | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-054o-9400001508-b91fc2f7328351b6aac5 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-002r-3600409808-0c9260d8dd5339a10235 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0lg1-1300409602-2d9eb77883a974b48a3b | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-07wd-2700819701-4afa8d141c2898762a90 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0zg4-2610001309-99091c7fe0e7157dc64a | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-052b-0902201504-be6a5a934c8098f360bd | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0f7c-9212301201-90e6edc17d313b937ab0 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0032892 |
|---|
| FooDB ID | FDB010874 |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 22370422 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 45360303 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | |
|---|