| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-05-22 06:02:38 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:15:58 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM019352 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Strontium ranelate heptahydrate |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Strontium ranelate, a strontium(II) salt of ranelic acid, is a medication for osteoporosis marketed as Protelos or Protos by Servier. Studies indicate it can also slow the course of osteoarthritis of the knee. The drug is unusual in that it both increases deposition of new bone by osteoblasts and reduces the resorption of bone by osteoclasts. It is therefore promoted as a "dual action bone agent" (DABA).
On 13 May 2013, Servier released a Direct Healthcare Professional Communication which stated that new restrictions for the use of strontium ranelate are now in place, as randomised trials have shown an increased risk of myocardial infarction. Servier states that the use is now restricted to treatment of severe osteoporosis in postmenopausal women at high risk for fracture. The European Pharmacovigilance Risk Assessment Committee (PRAC) recommends restriction in the use of strontium ranelate, based on a routine benefit-risk assessment of the medicine, which included data showing an increased risk of heart problems, including heart attacks. On 21 February 2014 the European Medicine Agency recommended that strontium ranelate remain available with restrictions relative to patients with existing heart disease. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | Not Available |
|---|
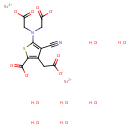
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Strontium ranelic acid | Generator | | 3-(3-Cyano-4-carboxymethyl-5-carboxy-2-thienyl)-3-azapentanedioic distrontium salt | MeSH | | Protelos | MeSH | | Strontium ranelate | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C12H20N2O15SSr2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 639.590 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 639.870 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 796104-87-5 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | distrontium(2+) ion 5-[bis(carboxylatomethyl)amino]-3-(carboxylatomethyl)-4-cyanothiophene-2-carboxylate heptahydrate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | distrontium(2+) ion 5-[bis(carboxylatomethyl)amino]-3-(carboxylatomethyl)-4-cyanothiophene-2-carboxylate heptahydrate |
|---|
| SMILES | O.O.O.O.O.O.O.[Sr++].[Sr++].[O-]C(=O)CN(CC([O-])=O)C1=C(C#N)C(CC([O-])=O)=C(S1)C([O-])=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C12H10N2O8S.7H2O.2Sr/c13-2-6-5(1-7(15)16)10(12(21)22)23-11(6)14(3-8(17)18)4-9(19)20;;;;;;;;;/h1,3-4H2,(H,15,16)(H,17,18)(H,19,20)(H,21,22);7*1H2;;/q;;;;;;;;2*+2/p-4 |
|---|
| InChI Key | BHMMKFQLHGVSRL-UHFFFAOYSA-J |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tetracarboxylic acids and derivatives. These are carboxylic acids containing exactly four carboxyl groups. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Tetracarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tetracarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tetracarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- 3,4,5-trisubstituted-2-aminothiophene
- Thiophene carboxylic acid
- Thiophene carboxylic acid or derivatives
- Dialkylarylamine
- 2-aminothiophene
- Thiophene
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Carboxylic acid salt
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Nitrile
- Carbonitrile
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic salt
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Appearance | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Strontium ranelate |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 24871329 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|