| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2016-05-22 05:45:07 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:15:54 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM019002 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Dutasteride |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Dutasteride is an oral synthetic 4-azasteroid commonly marketed under the trade name Avodart. It is a novel dual 5α-reductase inhibitor that works by blocking both isoforms of 5α-reductase enzymes in a potent, selective, and irreversible manner. Type I and II 5α-reductase enzymes convert testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a primary hormonal mediator that plays a role in the development and enlargement of the prostate gland. Dutasteride was approved by the FDA in 2001 for the treatment of symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) in men as monotherapy or in combination with the α-adrenergic antagonist to enhance the therapeutic response. Its clinical efficacy against benign prostate hyperplasia in male patients is comparable to that of , a specific type II 5α-reductase inhibitor. However, unlike finasteride, dutasteride is not yet indicated for the treatment of androgenic alopecia although it was demonstrated to be effective in several randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials in androgenetic alopecia. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - HMDB Contaminants - Urine
- STOFF IDENT Compounds
- ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | Not Available |
|---|
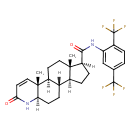
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (5alpha,17beta)-N-(2,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-oxo-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide | ChEBI | | alpha,alpha,alpha,Alpha',alpha',alpha'-hexafluoro-3-oxo-4-aza-5alpha-androst-1-ene-17beta-carboxy-2',5'-xylidide | ChEBI | | Avodart | Kegg | | (5a,17b)-N-(2,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-oxo-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide | Generator | | (5Α,17β)-N-(2,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl)-3-oxo-4-azaandrost-1-ene-17-carboxamide | Generator | | a,a,a,Alpha',alpha',alpha'-hexafluoro-3-oxo-4-aza-5a-androst-1-ene-17b-carboxy-2',5'-xylidide | Generator | | Α,α,α,alpha',alpha',alpha'-hexafluoro-3-oxo-4-aza-5α-androst-1-ene-17β-carboxy-2',5'-xylidide | Generator | | 17beta-N-(2,5-Bis(trifluoromethyl))phenyl-carbamoyl-4-aza-5alpha-androst-1-en-3-one | HMDB | | 745, GG | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C27H30F6N2O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 528.530 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 528.221 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 164656-23-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (1S,2R,7R,10S,11S,14S,15S)-N-[2,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-2,15-dimethyl-5-oxo-6-azatetracyclo[8.7.0.0²,⁷.0¹¹,¹⁵]heptadec-3-ene-14-carboxamide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | dutasteride |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]1(CC[C@@]2([H])[C@]3([H])CC[C@@]4([H])NC(=O)C=C[C@]4(C)[C@@]3([H])CC[C@]12C)C(=O)NC1=CC(=CC=C1C(F)(F)F)C(F)(F)F |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C27H30F6N2O2/c1-24-11-9-17-15(4-8-21-25(17,2)12-10-22(36)35-21)16(24)6-7-19(24)23(37)34-20-13-14(26(28,29)30)3-5-18(20)27(31,32)33/h3,5,10,12-13,15-17,19,21H,4,6-9,11H2,1-2H3,(H,34,37)(H,35,36)/t15-,16-,17-,19+,21+,24-,25+/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | JWJOTENAMICLJG-QWBYCMEYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as androgens and derivatives. These are 3-hydroxylated C19 steroid hormones. They are known to favor the development of masculine characteristics. They also show profound effects on scalp and body hair in humans. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Steroids and steroid derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Androstane steroids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Androgens and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Androgen-skeleton
- 3-oxosteroid
- 3-oxo-4-azasteroid
- 3-oxo-5-alpha-steroid
- Oxosteroid
- 4-azasteroid
- Azasteroid
- Trifluoromethylbenzene
- Anilide
- N-arylamide
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Carboxamide group
- Lactam
- Secondary carboxylic acid amide
- Azacycle
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Organohalogen compound
- Alkyl halide
- Alkyl fluoride
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organofluoride
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Not Available |
|---|
| Appearance | Not Available |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0r00-0695380000-37d765dda5ec5e49b0fd | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-0010190000-3420a2295d7f96d1d3c8 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0w4i-0566290000-0b4c4c43a1363f4cde3c | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0fka-2490010000-583fa26158a6ee3f69db | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0000090000-6590720379fb16a92f43 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-004i-1050090000-ceadcb8345b10a444f0f | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0kbf-2190000000-a71ffb6ab0e5ccfce59b | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-0001090000-69b701f7be2c2462c87c | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00b9-0594370000-8a9228b409aa1db36766 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-00xr-0590000000-e41abf0c7f5b9d8fd56d | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-0000090000-754362aa78fcb9885806 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-004i-1020090000-9af76f2aa77fb2cdadf5 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-004i-0040090000-5354ee6cb84f313f4a81 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Not Available |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01126 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0015258 |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Dutasteride |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 5293502 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 521033 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 6918296 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | |
|---|