| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-10-02 22:21:04 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:09:15 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM003925 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hydrogen Sulfate |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Sulfuric acid is a highly corrosive strong mineral acid with the molecular formula H2SO4. It is a pungent-ethereal, colorless to slightly yellow viscous liquid which is soluble in water at all concentrations. Sometimes, it is dyed dark brown during production to alert people to its hazards. The historical name of this acid is oil of vitriol.
Concentrated sulfuric acid is 98% pure and shows different properties depending upon its concentration. For instance battery acid is 30% sulfuric acid. Because the hydration reaction of sulfuric acid is highly exothermic, dilution should always be performed by adding the acid to the water rather than the water to the acid. Pure sulfuric acid is not encountered naturally on Earth in its anhydrous form, due to its great affinity for water. Dilute sulfuric acid is a constituent of acid rain, which is formed by atmospheric oxidation of sulfur dioxide in the presence of water – i.e., oxidation of sulfurous acid. Sulfur dioxide is the main byproduct produced when sulfur-containing fuels such as coal or oil are burned. Most sulfuric acid (~60%) is consumed for fertilizers, particularly superphosphates, ammonium phosphate and ammonium sulfates. About 20% is used in chemical industry for production of detergents, synthetic resins, dyestuffs, pharmaceuticals, petroleum catalysts, insecticides and antifreeze, as well as in various processes such as oil well acidicizing, aluminium reduction, paper sizing, water treatment.
|
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - STOFF IDENT Compounds
- T3DB toxins
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Fertilizer
- Industrial/Workplace Toxin
- Lachrymator
- Natural Compound
|
|---|
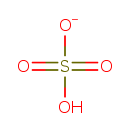
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| [SO3(OH)](-) | ChEBI | | HSO4(-) | ChEBI | | HYDROGEN sulfATE | ChEBI | | HYDROGEN sulfuric acid | Generator | | HYDROGEN sulphate | Generator | | HYDROGEN sulphuric acid | Generator | | Hydrogensulfuric acid | Generator | | Hydrogensulphate | Generator | | Hydrogensulphuric acid | Generator |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | HO4S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 97.071 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 96.960 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | Not Available |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | hydrogen sulfate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | hydrogen sulfate |
|---|
| SMILES | OS([O-])(=O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/H2O4S/c1-5(2,3)4/h(H2,1,2,3,4)/p-1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | QAOWNCQODCNURD-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as non-metal sulfates. These are inorganic non-metallic compounds containing a sulfate as its largest oxoanion. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Homogeneous non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Class | Non-metal oxoanionic compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Non-metal sulfates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Non-metal sulfates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Non-metal sulfate
- Inorganic oxide
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Not Available |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Liquid |
|---|
| Appearance | Colorless liquid, sometimes, it is dyed dark brown during production to alert people to its hazards |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 10°C | | Boiling Point | 337°C | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0002-9000000000-e4491aa733acdbf89855 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0002-9000000000-30255ae62c4d201e0c76 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0002-9000000000-9d86e3695e6acb0f89b1 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0002-9000000000-c7a86b5fa5f68d2b74cb | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0002-9000000000-4ac8d9e17977ddac3bd9 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0002-9000000000-f59382cd8927bc78f4c4 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Inhalation; Ingestion; Dermal; Eyes |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Many strong acids cause tissue burns through the denaturation of proteins and partial hydrolysis of proteins. Most proteins denature at pH values of less than 3-4. The large-scale denaturation of proteins, de-esterification of lipids and subsequent desiccation of tissues leads to chemical burns. Symptoms include itching, bleaching or darkening of skin or tissues, blistering and burning sensations. More specifically, sulfuric acid readily decomposes proteins and lipids through amide hydrolysis and ester hydrolysis upon contact with living tissues. In addition, it exhibits a strong dehydrating property on carbohydrates, liberating extra heat and causing secondary thermal burns. The strong oxidizing property may also extend its corrosiveness on the tissue. Because of such reasons, damage posed by sulfuric acid is potentially more severe than that caused by other comparable strong acids, such as hydrochloric acid and nitric acid. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Acute oral toxicity (LD50): 2140 mg/kg [Rat.]. Acute toxicity of the vapor (LC50): 320 mg/m3 for 2 hours [Mouse] |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | Occupational exposures to strong inorganic acid mists containing sulfuric acid are carcinogenic to humans (Group 1). (1) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Sulfuric acid is found naturally in acid rain or rainwater near industrial sites. Most sulfuric acid (~60%) is consumed for fertilizers, particularly superphosphates, ammonium phosphate and ammonium sulfates. About 20% is used in chemical industry for production of detergents, synthetic resins, dyestuffs, pharmaceuticals, petroleum catalysts, insecticides and antifreeze, as well as in various processes such as oil well acidicizing, aluminium reduction, paper sizing, water treatment. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | The limit of exposure of sulfuric acid is fixed at 1 mg/m3 |
|---|
| Health Effects | Sulfuric acid at a high concentration can cause very serious damage upon contact, as it not only causes chemical burns via hydrolysis, but also secondary thermal burns via dehydration. It burns the cornea and can lead to permanent blindness if splashed onto eyes. Accordingly, it rapidly attacks the cornea and can induce permanent blindness if splashed onto eyes. If ingested, it damages internal organs irreversibly and may even be fatal. Inhalation of sulfuric acid spray mist may produce severe irritation of respiratory tract, characterized by coughing, choking, or shortness of breath. Sulfuric acid is also a known carcinogen. Sulfuric acid may be toxic to kidneys, lungs, heart, cardiovascular system, upper respiratory tract, eyes and teeth. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Skin contact can cause redness, pain, blisters and severe skin burns. Sulfuric acid may cause severe burns to the eye and permanent eye damage. Severe and rapid corrosive burns of the mouth, gullet and gastrointestinal tract will result if sulfuric acid is swallowed. Symptoms include burning, choking, nausea, vomiting and severe pain. |
|---|
| Treatment | The mainstay of treatment of any acid burn is copious irrigation with large amounts of tap water. To be most effective, treatment should be started immediately after exposure, preferably before arrival in the emergency department. Remove any contaminated clothing. Do not attempt to neutralize the burn with weak reciprocal chemicals (i.e. alkali for acid burns), because the heat generated from the chemical reaction may cause severe thermal injury. |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 45696 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 61778 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|