| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-09-17 20:02:20 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:09:14 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM003905 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Disodium tetraborate, anhydrous |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Borax, also known as sodium borate, sodium tetraborate, or disodium tetraborate, has a wide variety of uses. It is a component of many detergents, cosmetics, and enamel glazes. It is also used to make buffer solutions in biochemistry, as a fire retardant, as an anti-fungal compound for fiberglass, as a flux in metallurgy, neutron-capture shields for radioactive sources, a texturing agent in cooking, and as a precursor for other boron compounds. In artisanal gold mining, the borax method is sometimes used as a substitute for toxic mercury in the gold extraction process.
Borax, sodium tetraborate decahydrate, according to one study, is not acutely toxic. Sodium tetraborate decahydrate was once registered as an insecticide for a brief period, and the product was issued a "Danger" signal word by the EPA. Registration was allowed to lapse after the initial one year registration due to the fact the product could not be legally sold over the counter as an insecticide due to the dangers the product posed to the general public. Danger is the highest level signal word issued by the EPA. Its LD50 (median lethal dose) score is tested at 2.66 g/kg in rats: a significant dose of the chemical is needed to cause severe symptoms or death. The lethal dose is not necessarily the same for humans.
Sufficient exposure to borax dust can cause respiratory and skin irritation. Ingestion may cause gastrointestinal distress including nausea, persistent vomiting, abdominal pain, and diarrhea. Effects on the vascular system and brain include headaches and lethargy, but are less frequent. "In severe poisonings, a beefy red skin rash affecting palms, soles, buttocks and scrotum has been described. With severe poisoning, erythematous and exfoliative rash, unconsciousness, respiratory depression, and renal failure."
Borax was added to the Substance of Very High Concern (SVHC) candidate list on 16 December 2010. The SVHC candidate list is part of the EU Regulations on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals 2006 (REACH), and the addition was based on the revised classification of borax as toxic for reproduction category 1B under the CLP Regulations. Substances and mixtures imported into the EU which contain borax are now required to be labelled with the warnings "May damage fertility" and "May damage the unborn child". (Wikipedia) |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - EAFUS Chemicals
- ECHA Toxic for reproduction
- HPV EPA Chemicals
- OECD HPV Chemicals
- T3DB toxins
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Cosmetic Toxin
- Industrial/Workplace Toxin
- Inorganic Compound
- Insecticide
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
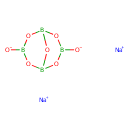
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Disodium bicyclo[3.3.1]tetraboroxane-3,7-bis(olic acid) | Generator | | Sodium diborate | MeSH | | Sodium tetraborate | MeSH | | Disodium borate, monohydrate | MeSH | | Sodium metaborate | MeSH | | Disodium borate, heptahydrate | MeSH | | Komex | MeSH | | Sodium borate | MeSH | | Sodium meta borate | MeSH | | Monosodium metaborate | MeSH | | Sodium borate (nabo2) | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | B4Na2O7 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 201.219 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 201.981 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 1303-96-4 and 1330-43-4 and 12179-04-3 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | disodium bicyclo[3.3.1]tetraboroxane-3,7-bis(olate) |
|---|
| Traditional Name | disodium bicyclo[3.3.1]tetraboroxane-3,7-bis(olate) |
|---|
| SMILES | [Na+].[Na+].[O-]B1OB2OB([O-])OB(O1)O2 |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/B4O7.2Na/c5-1-7-3-9-2(6)10-4(8-1)11-3;;/q-2;2*+1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | UQGFMSUEHSUPRD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of inorganic compounds known as alkali metal borates. These are inorganic compounds in which the largest oxoanion is borate, and in which the heaviest atom not in an oxoanion is an alkali metal. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Inorganic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Mixed metal/non-metal compounds |
|---|
| Class | Alkali metal oxoanionic compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Alkali metal borates |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alkali metal borates |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Borate
- Alkali metal borate
- Inorganic sodium salt
- Inorganic oxide
- Inorganic salt
- Inorganic metalloid salt
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Not Available |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | Powdered borax is white, consisting of soft colorless crystals that dissolve easily in water. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0090000000-89d75eccb0d5c687676b | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0090000000-d67b53e737a4f2817c2d | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0udi-4090000000-cb876ca5e86588f3f600 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Borax is a component of many detergents, cosmetics, and enamel glazes. It is also used to make buffer solutions in biochemistry, as a fire retardant, as an anti-fungal compound for fiberglass, as a flux in metallurgy, neutron-capture shields for radioactive sources, a texturing agent in cooking, and as a precursor for other boron compounds. In artisanal gold mining, the borax method is sometimes used as a substitute for toxic mercury in the gold extraction process. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DBSALT002513 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 10219853 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|