| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-09-11 05:15:44 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:09:12 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM003724 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Hydroxyurea |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | An antineoplastic agent that inhibits DNA synthesis through the inhibition of ribonucleoside diphosphate reductase. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - HMDB Contaminants - Urine
- IARC Carcinogens Group 3
- STOFF IDENT Compounds
- T3DB toxins
- ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amine
- Antineoplastic Agent
- Antisickling Agent
- Drug
- Enzyme Inhibitor
- Metabolite
- Nucleic Acid Synthesis Inhibitor
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
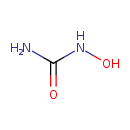
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Carbamohydroxamic acid | ChEBI | | Carbamohydroximic acid | ChEBI | | Carbamoyl oxime | ChEBI | | Carbamyl hydroxamate | ChEBI | | Hidroxicarbamida | ChEBI | | Hydrea | ChEBI | | Hydroxycarbamid | ChEBI | | Hydroxycarbamide | ChEBI | | Hydroxycarbamidum | ChEBI | | Hydroxyharnstoff | ChEBI | | N-Carbamoylhydroxylamine | ChEBI | | N-HYDROXYUREA | ChEBI | | Oxyurea | ChEBI | | Droxia | Kegg | | Carbamohydroxamate | Generator | | Carbamohydroximate | Generator | | Carbamyl hydroxamic acid | Generator | | Carbamohydroxyamic acid | HMDB | | HU | HMDB | | Hydroxicarbamidum | HMDB | | Hydroxycarbamine | HMDB | | Hydroxylurea | HMDB | | Idrossicarbamide | HMDB | | Oncocarbide | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | CH4N2O2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 76.055 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 76.027 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 127-07-1 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | hydroxyurea |
|---|
| Traditional Name | hydroxyurea |
|---|
| SMILES | NC(=O)NO |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/CH4N2O2/c2-1(4)3-5/h5H,(H3,2,3,4) |
|---|
| InChI Key | VSNHCAURESNICA-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as carboximidic acids and derivatives. Carboximidic acids and derivatives are compounds containing a carboximidic group, with the general formula R-C(=NR1)OR2. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboximidic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Carboximidic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Carboximidic acid derivative
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Imine
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 133-136°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 1E+006 mg/L (at 25°C) |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (3 TMS) | splash10-0059-3950000000-0418fbb00ea645e9e0ce | Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0059-3950000000-0418fbb00ea645e9e0ce | Spectrum | | GC-MS | GC-MS Spectrum - GC-EI-TOF (Non-derivatized) | splash10-0002-0920000000-be691e1a11d76d687cc5 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-725178d2fb4e3ae0a710 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-15e079ef519fdae75dab | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , positive | splash10-03di-9000000000-f39d1396b2b03d5846c8 | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , positive | splash10-01ox-9000000000-b5fb6577ca88b375ebea | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ , positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-6093ebde62cb84552dd0 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-9000000000-5f85466dc663205c60f9 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-056r-9000000000-fb233b42b45077d2475d | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-06tf-9000000000-868a329446e04867fc56 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-004i-9000000000-6245f3456e3558782716 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-722afb6d05d2ca0794f5 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-f6792fcc64ed7bdb2466 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-004i-9000000000-fbd92a2a1457de08f558 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-01r6-9000000000-ff7708ba70751a23d1eb | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-fd9f25340762315b4515 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-90726b17dc36e29c5299 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-90726b17dc36e29c5299 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0006-9000000000-90726b17dc36e29c5299 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Hydroxyurea is converted to a free radical nitroxide (NO) in vivo, and transported by diffusion into cells where it quenches the tyrosyl free radical at the active site of the M2 protein subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, inactivating the enzyme. The entire replicase complex, including ribonucleotide reductase, is inactivated and DNA synthesis is selectively inhibited, producing cell death in S phase and synchronization of the fraction of cells that survive. Repair of DNA damaged by chemicals or irradiation is also inhibited by hydroxyurea, offering potential synergy between hydroxyurea and radiation or alkylating agents. Hydroxyurea also increases the level of fetal hemoglobin, leading to a reduction in the incidence of vasoocclusive crises in sickle cell anemia. Levels of fetal hemoglobin increase in response to activation of soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC) by hydroxyurea-derived NO. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Hepatic.
Route of Elimination: Renal excretion is a pathway of elimination.
Half Life: 3-4 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Oral, mouse: LD50 = 7330 mg/kg; Oral, rat: LD50 = 5760 mg/kg |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 3, not classifiable as to its carcinogenicity to humans. (1) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For management of melanoma, resistant chronic myelocytic leukemia, and recurrent, metastatic, or inoperable carcinoma of the ovary and Sickle-cell anemia. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Teratogenicity: Teratogenic effects have occurred in experimental animals. Hydroxyurea use during a small number of human pregnancies has been reported. Adverse effects have not been observed in any of the exposed newborns.
Reproductive Effects: Adverse reproductive effects have occurred in experimental animals.
Mutagenicity: Mutagenic effects have occurred in experimental animals.Mutagenic effects have occurred in humans. |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01005 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0015140 |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | HYDROXY-UREA |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | NHY |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Hydroxyurea |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 3530 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 44423 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 3657 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | C07044 |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Dee W. Brooks, Andrew O. Stewart, Richard A. Craig, “Substituted aryl- and heteroarylalkenyl-N-hydroxyurea inhibitors of leukotriene biosynthesis.” U.S. Patent US5506261, issued October, 1990. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | |
|---|