| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-30 21:05:24 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:09:09 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM003526 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Camazepam |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Camazepam is a benzodiazepine which is a dimethyl carbamate ester of tamzepam, a metabolite of diazepam. Similarly to other drugs in its class, it has antxiolytic, anticonvulsant, hypnotic, and skeletal muscle relaxant properties. However, unlike other benzodiapeines camazepam is predominantly anxiolytic and is relatively weak as an anticonvulsant, hypnotic and skeletal muscle relaxant. Camazepam also has less side effects, such as impaired cognition and reaction times, compared to other benzodiazepines. However, impairment of cognition and disrupted sleep patterns will occur at doses higher than 40mg of carazepam.]Camazepam is also believed to increase attention, and is associated with skin disorders. In the United States camazepam is regulated as a Schedule IV controlled substance. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - STOFF IDENT Compounds
- T3DB toxins
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Benzodiazepine
- Drug
- Ether
- Hypnotic and Sedative
- Neuromuscular Agent
- Organic Compound
- Organochloride
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
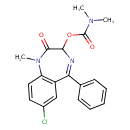
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C19H18ClN3O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 371.818 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 371.104 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 36104-80-0 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | 7-chloro-1-methyl-2-oxo-5-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-1,4-benzodiazepin-3-yl N,N-dimethylcarbamate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | camazepam |
|---|
| SMILES | CN(C)C(=O)OC1N=C(C2=CC=CC=C2)C2=C(C=CC(Cl)=C2)N(C)C1=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C19H18ClN3O3/c1-22(2)19(25)26-17-18(24)23(3)15-10-9-13(20)11-14(15)16(21-17)12-7-5-4-6-8-12/h4-11,17H,1-3H3 |
|---|
| InChI Key | PXBVEXGRHZFEOF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 1,4-benzodiazepines. These are organic compounds containing a benzene ring fused to a 1,4-azepine. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Benzodiazepines |
|---|
| Sub Class | 1,4-benzodiazepines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 1,4-benzodiazepines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 1,4-benzodiazepine
- Alpha-amino acid or derivatives
- Aryl chloride
- Aryl halide
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Carbamic acid ester
- Tertiary carboxylic acid amide
- Carboxamide group
- Ketimine
- Lactam
- Carbonic acid derivative
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Imine
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxide
- Organohalogen compound
- Organochloride
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organooxygen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 173-174°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-1009000000-823c63921e078c0416db | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00dj-4129000000-882e1f6e37c13e988a26 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0007-9620000000-4f609372fd4f6171c750 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-00di-3029000000-d4cb6289ec62182ee71e | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0089-2079000000-10339e966393eac9544e | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00y3-9000000000-e9c3496236445c282b83 | Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-00di-9260000000-edfba1a5fcbe9ca50d1d | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Almost completely absorbed into the bloodstream after oral administration. 90% bioavailability can be achieved in humans. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Camazepam has been shown to bind competitively to benzodiazepine receptors in the brain with a relatively low affinity in animal models. This binding of benzodiazepine receptors by camazepam and its active metabolites is responsible for its anticonvulsant effects. Notably, only three metabolites were shown to exert anticonvulsant activity, temazepam, oxazepam, and hydroxy camazepam. The anxiolytic properties of camazepam are also attributed to their ability to bind benzodiazepine receptors, also known as GABA receptors. When benzodiazepines bind to GABA receptors they increase the efficiency with which the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA binds. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Metabolized by the liver into more than 10 metabolites, some of which are also active and posses anticonvulsant properties. [3] One active metabolite of note is temazepam which has roughly equal in effectiveness as an anxiolytic, but is less anticonvulsant, sedating, and motor-impairing.
Camazepam undergoes enantioselective metabolism by human liver microsomes. [1]
Route of Elimination: Renally eliminated. |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Camazepam has been used in placebo controlled studies for the treatment of patients suffering from anxiety and depression. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | General supportive measures should be employed, along with intravenous fluids, and an adequate airway maintained. Hypotension may be combated by the use of norepinephrine or metaraminol. Dialysis is of limited value. Flumazenil (Anexate) is a competitive benzodiazepine receptor antagonist that can be used as an antidote for benzodiazepine overdose. In particular, flumazenil is very effective at reversing the CNS depression associated with benzodiazepines but is less effective at reversing respiratory depression. Its use, however, is controversial as it has numerous contraindications. It is contraindicated in patients who are on long-term benzodiazepines, those who have ingested a substance that lowers the seizure threshold, or in patients who have tachycardia or a history of seizures. As a general rule, medical observation and supportive care are the mainstay of treatment of benzodiazepine overdose. Although benzodiazepines are absorbed by activated charcoal, gastric decontamination with activated charcoal is not beneficial in pure benzodiazepine overdose as the risk of adverse effects often outweigh any potential benefit from the procedure. It is recommended only if benzodiazepines have been taken in combination with other drugs that may benefit from decontamination. Gastric lavage (stomach pumping) or whole bowel irrigation are also not recommended. |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB01489 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Camazepam |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 37367 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Ferrari, G. and Casagrande, C.; U.S. Patent 3,799,920; March 26,1974; assigned to Siphar SA. |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|