| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2014-08-29 04:49:23 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:09:01 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM002984 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | L-Hypoglycin A |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Hypoglycin is toxic if ingested and is the causative agent of Jamaican vomiting sickness. It is an amino acid and chemically related to lysine. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - FooDB Chemicals
- T3DB toxins
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amine
- Food Toxin
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
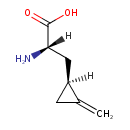
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Hypoglycin a | Kegg | | Hypoglycine a | Kegg | | L-Hypoglycin | Kegg | | Hypoglycin, (S)-isomer | MeSH | | Hypoglycin | MeSH | | Hypoglycin, carboxy-(14)C-labeled | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C7H11NO2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 141.168 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 141.079 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 156-56-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S)-2-amino-3-[(1S)-2-methylidenecyclopropyl]propanoic acid |
|---|
| Traditional Name | hypoglycin |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@](N)(C[C@]1([H])CC1=C)C(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C7H11NO2/c1-4-2-5(4)3-6(8)7(9)10/h5-6H,1-3,8H2,(H,9,10)/t5-,6-/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | OOJZCXFXPZGUBJ-WDSKDSINSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as l-alpha-amino acids. These are alpha amino acids which have the L-configuration of the alpha-carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Amino acids, peptides, and analogues |
|---|
| Direct Parent | L-alpha-amino acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - L-alpha-amino acid
- Carbocyclic fatty acid
- Fatty acyl
- Amino acid
- Carboxylic acid
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary amine
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Amine
- Primary aliphatic amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Aliphatic homomonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic homomonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB Link | KEGG Link |
|---|
| Insulin secretion | Not Available | map04911 |
|
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0005-9700000000-88f654ad511bd615f974 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0002-9100000000-a638d182cec2d0f2e025 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0gb9-9000000000-bf3e574de9d48c765285 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-1900000000-0947306f5db224c96483 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-006x-8900000000-f72f90f16257f62431a4 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-00di-9000000000-762784d2a97818f41e95 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Generally, hypoglycin is an amino acid and chemically related to lysine. It competitively binds to enzymes used in the catabolism of lysine and is the reason why it and its metabolitemethylene cyclopropyl acetic acid (MCPA) are toxic. The metabolite MCPA also is a potent inhibitor of acyl CoA dehydrogenase, preventing the metabolism of fatty acids. It has been shown that oxidation of leucine is inhibited by hypoglycin A. In contrast, oxidation of valine and isoleucine are not significantly inhibited by this compound. However, the specific step in the pathway of leucine metabolism that is inhibited by hypoglycin A has not been precisely identified. Hypoglycemia and depletion of glycogen were due to the decreased gluconeogenesis resulting from impairment of long chain fatty acid metabolism after injection of hypoglycin A. Hypoglycin A or its metabolite, methylenecyclopropylacetic acid, and also 4-pentenoic acid (4-PE) were shown to inhibit long-chain fatty acid oxidation; whereas oxidation of straight short chain fatty acids including butyrate, hexanoate, and octanoate was not inhibited. Hypolglycin A inhibits dehydrogenation of isovaleryl-CoA and alpha-methylbutyryl-CoA by liver slices in vitro, and that it induces isovaleric and alpha-methylbutyric acidemias in experimental animals in vivo. (PMID: 4636318; PMID:5276292) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | C00001372 |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Hypoglycin A |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 441451 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | C08287 |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|