| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2013-04-25 07:56:55 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:59 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM002893 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Thiamethoxam |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Thiamethoxam is a neonicotinoid insecticide, which is a class of neuro-active insecticides modeled after nicotine. Nicotine was identified and used as an insecticide and rat poison as early as the 1600’s. Its effectiveness as an insecticide spurred a search for insecticidal compounds that have selectively less effect on mammals, which led to the discovery of neonicotinoids. Neonicotinoids, like nicotine, bind to nicotinic acetylcholine receptors of a cell. In mammals, nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are located in cells of both the central and peripheral nervous systems. In insects these receptors are limited to the CNS. While low to moderate activation of these receptors causes nervous stimulation, high levels overstimulate and block the receptors causing paralysis and death. Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are activated by the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Acetylcholine is broken down by acetylcholinesterase to terminate signals from these receptors. However, acetylcholinesterase cannot break down neonicotinoids and the binding is irreversible. Because most neonicotinoids bind much more strongly to insect neuron receptors than to mammal neuron receptors, these insecticides are selectively more toxic to insects than mammals. The low mammalian toxicity of neonicotinoids can be explained in large part by their lack of a charged nitrogen atom at physiological pH. The uncharged molecule can penetrate the insect blood–brain barrier, while the mammalian blood–brain barrier filters it. However, Some neonicotinoid breakdown products are toxic to humans, especially if they have become charged. Because of their low toxicity and other favorable features, neonicotinoids are among the most widely used insecticides in the world. Most neonicotinoids are water-soluble and break down slowly in the environment, so they can be taken up by the plant and provide protection from insects as the plant grows. Neonicotinoids are currently used on corn, canola, cotton, sorghum, sugar beets and soybeans. They are also used on the vast majority of fruit and vegetable crops, including apples, cherries, peaches, oranges, berries, leafy greens, tomatoes, and potatoes. The use of neonicotinoids has been linked in a range of studies to adverse ecological effects, including honey-bee colony collapse disorder (CCD) and loss of birds due to a reduction in insect populations. This has led to moratoriums and bans on their use in Europe. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - STOFF IDENT Compounds
- T3DB toxins
- ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amine
- Ether
- Insecticide
- Organic Compound
- Organochloride
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
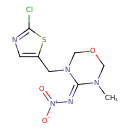
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| ACTARA 25 WG | MeSH | | 3-(2-chloro-Thiazol-5-ylmethyl)-5-methyl-(1,3,5)oxadiazinan-4-yldene-N-nitroamine | MeSH | | Actara | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C8H10ClN5O3S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 291.715 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 291.019 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 153719-23-4 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (4Z)-3-[(2-chloro-1,3-thiazol-5-yl)methyl]-5-methyl-N-nitro-1,3,5-oxadiazinan-4-imine |
|---|
| Traditional Name | thiamethoxam |
|---|
| SMILES | CN1COCN(CC2=CN=C(Cl)S2)\C1=N/[N+]([O-])=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C8H10ClN5O3S/c1-12-4-17-5-13(8(12)11-14(15)16)3-6-2-10-7(9)18-6/h2H,3-5H2,1H3/b11-8- |
|---|
| InChI Key | NWWZPOKUUAIXIW-FLIBITNWSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as 2,5-disubstituted thiazoles. 2,5-disubstituted thiazoles are compounds containing a thiazole ring substituted at positions 2 and 5 only. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Azoles |
|---|
| Sub Class | Thiazoles |
|---|
| Direct Parent | 2,5-disubstituted thiazoles |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - 2,5-disubstituted 1,3-thiazole
- Aryl chloride
- Aryl halide
- Heteroaromatic compound
- Guanidine
- Organic nitro compound
- Allyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Oxacycle
- Azacycle
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organochloride
- Organohalogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Aromatic heteromonocyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteromonocyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 139.1°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ 10V, positive | splash10-01ox-0090000000-b96956c5f01f7b4d87b8 | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ 20V, positive | splash10-001i-0930000000-c2368eb9e2ec01afe97d | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ 30V, positive | splash10-001i-0900000000-d8c26cd5c80e6ba67455 | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - LC-ESI-QQ 40V, positive | splash10-053r-0900000000-29bc8a1fa27dbbd0e44b | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0006-0090000000-9352dc604b386f6ac9a1 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000x-1090000000-3bb13ae0dfd8f9be65ec | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-03di-6900000000-1b53cccfd2735db5c0df | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-3090000000-958ae188a575a58163bc | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9100000000-5621eb62e7c5584c2a8a | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0a4l-9200000000-6c00dbb61be83b615c66 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Not Available |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | This is a man-made compound that is used as a pesticide. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Thiamethoxam |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5485188 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|