| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2013-04-25 07:56:50 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:58 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM002780 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Cymoxanil |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Cyomaxinil is a fungicide which was first introduced in 1977. It is an acetimide compound used as both a curative and preventative foliar fungicide. In Europe it is being sold for use on grapes, potatoes, tomatoes, hops, sugarbeets and other vegetable crops. Cymoxanil is currently not registered in the U.S. Cymoxanil's mode of action is as a local systemic. It penetrates rapidly and when inside the plant, it cannot be washed off by rain. It controls diseases during the incubation period and prevents the appearance of damage on the crop. The fungicide is primarily active on fungi belonging to the Peronosporales order: Phytophthora, Plasmopara, and Peronospora. Cymoxanil has low acute and chronic toxicity |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - HPV EPA Chemicals
- My Exposome Chemicals
- STOFF IDENT Compounds
- T3DB toxins
- ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Ether
- Fungicide
- Nitrile
- Organic Compound
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
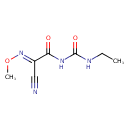
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| 2-cyano-N-((ethylamino)Carbonyl)-2-(methoxyimino)acetamide | MeSH | | Curzate | MeSH | | DPX 3217 Fumarate | MeSH | | DPX 3217 Copper sulfate | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C7H10N4O3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 198.179 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 198.075 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 57966-95-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (E)-2-[(ethylcarbamoyl)amino]-2-oxoethenecarbonimidoyl cyanide |
|---|
| Traditional Name | cymoxanil |
|---|
| SMILES | CCNC(=O)NC(=O)C(=N\OC)\C#N |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C7H10N4O3/c1-3-9-7(13)10-6(12)5(4-8)11-14-2/h3H2,1-2H3,(H2,9,10,12,13)/b11-5+ |
|---|
| InChI Key | XERJKGMBORTKEO-VZUCSPMQSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as oxime ethers. Oxime ethers are compounds containing the oxime ether functional group, with the general structure R1(R2)C=NOR3 ( R3 not H). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic nitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Class | Organonitrogen compounds |
|---|
| Sub Class | Oximes |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Oxime ethers |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Oxime ether
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Nitrile
- Carbonitrile
- Carboximidic acid derivative
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | - Aliphatic nitrogen fungicides (C18498 )
|
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0007-9500000000-532af03a1145ff0f87ab | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-000f-9200000000-bf649946370878b70b40 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-736c4f705aeb8ff652ce | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-002e-4900000000-c539bff4c0b9bb3d6a63 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-00pm-9600000000-1f7d79ce477d3c6a0bd3 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0f7o-9000000000-cc1db7899c76f6131f59 | Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-000x-9200000000-9b9b169f8f384bec01e9 | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 13C NMR Spectrum | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Organic nitriles decompose into cyanide ions both in vivo and in vitro. Consequently the primary mechanism of toxicity for organic nitriles is their production of toxic cyanide ions or hydrogen cyanide. Cyanide is an inhibitor of cytochrome c oxidase in the fourth complex of the electron transport chain (found in the membrane of the mitochondria of eukaryotic cells). It complexes with the ferric iron atom in this enzyme. The binding of cyanide to this cytochrome prevents transport of electrons from cytochrome c oxidase to oxygen. As a result, the electron transport chain is disrupted and the cell can no longer aerobically produce ATP for energy. Tissues that mainly depend on aerobic respiration, such as the central nervous system and the heart, are particularly affected. Cyanide is also known produce some of its toxic effects by binding to catalase, glutathione peroxidase, methemoglobin, hydroxocobalamin, phosphatase, tyrosinase, ascorbic acid oxidase, xanthine oxidase, succinic dehydrogenase, and Cu/Zn superoxide dismutase. Cyanide binds to the ferric ion of methemoglobin to form inactive cyanmethemoglobin. (2) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Organic nitriles are converted into cyanide ions through the action of cytochrome P450 enzymes in the liver. Cyanide is rapidly absorbed and distributed throughout the body. Cyanide is mainly metabolized into thiocyanate by either rhodanese or 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfur transferase. Cyanide metabolites are excreted in the urine. (1) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | This is a man-made compound that is used as a pesticide. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | Not Available |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 5364079 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | C18498 |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|