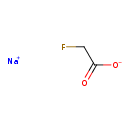| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-08-12 14:05:03 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:53 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM002563 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Sodium fluoroacetate |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Sodium fluoroacetate is an organofluorine compound and a derivative of fluoroacetic acid. Sodium fluoroacetate is known under its brand name "1080". Sodium fluoroacetate occurs naturally as an anti-herbivore metabolite in various plants but can also be produced synthetically. Fluoroacetate is highly toxic to mammals and insects; it is used as a pesticide especially for mammalian pest species. The more common fluorinated acetic acid, trifluoroacetic acid and its sodium salt are far less toxic. (2) |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - Clean Air Act Chemicals
- HPV EPA Chemicals
- T3DB toxins
- ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Organic Compound
- Organofluoride
- Pesticide
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Fluoroacetic acid sodium salt | ChEBI | | Natriumfluoracetat | ChEBI | | Sodium monofluoroacetate | ChEBI | | Fluoroacetate sodium salt | Generator | | Sodium monofluoroacetic acid | Generator | | Sodium fluoroacetic acid | Generator | | Fluoroacetic acid, aluminum salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, barium salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, mercury (2+) salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, terbium (+3) salt | MeSH | | Monofluoroacetate | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, ammonium salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, ammonium salt, 2-(14)C-labeled | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, copper (2+) salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, lead (+4) salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, magnesium salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, sodium salt | MeSH | | Monofluoroacetic acid | MeSH | | Sodium (18F)fluoroacetate | MeSH | | Compound 1080 | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, 18F-labeled | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, cadmium salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, calcium salt | MeSH | | Fluoroacetic acid, potassium salt | MeSH |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C2H2FNaO2 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 100.024 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 99.994 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 62-74-8 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | sodium 2-fluoroacetate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | sodium fluoroacetate |
|---|
| SMILES | [Na+].[O-]C(=O)CF |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C2H3FO2.Na/c3-1-2(4)5;/h1H2,(H,4,5);/q;+1/p-1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | JGFYQVQAXANWJU-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as alpha-halocarboxylic acids. These are carboxylic acids containing a halogen atom bonded to the alpha carbon atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Carboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Alpha-halocarboxylic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Alpha-halocarboxylic acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Alpha-halocarboxylic acid
- Carboxylic acid salt
- Organic metal halide
- Carboxylic acid
- Organic alkali metal salt
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Alkyl fluoride
- Organic salt
- Organooxygen compound
- Organofluoride
- Organohalogen compound
- Organic sodium salt
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxygen compound
- Alkyl halide
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | Odourless white powder. (1) |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 200°C (325.15°K) | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-6900000000-569a907c8575fb953c9d | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0pb9-9500000000-f6612ed8e54151211376 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0006-9000000000-c38f4fc2aa6d983aaf82 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0002-9000000000-b1353035c7679a46035c | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0002-9000000000-ec2e810004e52259cc30 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0002-9000000000-69a83ef6cd4d50dd12c6 | Spectrum | | 1D NMR | 1H NMR Spectrum | Not Available | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Not Available |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Fluoroacetate is similar to acetate, which has a pivotal role in cellular metabolism. Fluoroacetate disrupts the citric acid cycle by combining with coenzyme A to form fluoroacetyl CoA. Fluoroacetyl CoA then reacts with citrate synthase to produce fluorocitrate. A metabolite of fluorocitrate binds very tightly to aconitase, thereby halting the citric acid cycle. This inhibition results in an accumulation of citrate in the blood which deprives cells of energy. (2) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Not Available |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Not Available |
|---|
| Symptoms | The symptoms of sodium fluoroacetate poisoning normally appear between 30 minutes and three hours after exposure. Initial symptoms typically include nausea, vomiting and abdominal pain; sweating, confusion and agitation follow. In significant poisoning cardiac abnormalities including tachycardia or bradycardia, hypotension and ECG changes develop. Neurological effects include muscle twitching and seizures. Consciousness becomes progressively impaired after a few hours leading to coma. Death is generally due to ventricular arrhythmias, progressive hypotension unresponsive to treatment, and secondary lung infections. Sub-lethal doses of sodium fluoroacetate may cause damage to tissues with high energy needs, in particular, the brain, gonads, heart, lungs and fetus. Sub-lethal doses are typically completely metabolised and excreted within four days. (2) |
|---|
| Treatment | Because of the biochemical interference in the citric acid cycle, sodium fluoroacetate poisoning is very difficult to treat. Once clinical symptoms are exhibited, the citric acid cycle has shut down. Effective antidotes are unknown. Research in animals has shown that the use of glyceryl monoacetate can prevent problems if given after ingestion of sodium fluoroacetate. In clinical cases, use of muscle relaxants, anti-convulsants, mechanical ventilation, and other supportive measures may all be required. Few animals or people have been treated successfully after significant sodium fluoroacetate ingestions. (2) |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Sodium fluoroacetate |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 38699 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 6123 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | C18588 |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|