| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-23 18:26:06 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:46 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM002416 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Aconitine |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Aconitine is a plant toxin found in species of wolfsbane (Aconitum genus). It is a neurotoxin previously used as an antipyretic and analgesic, and still has some limited application in herbal medicine. (1). The toxic effects of Aconitine have been tested in a variety of different test animals, including mammals (dog, cat, guinea pig, mouse, rat and rabbit), frogs and pigeons. Depending on the route of exposure, the observed toxic effects were: local anesthetic effect, diarrhea, convulsions, arrhythmias or death. According to a review of different reports of aconite poisoning in humans the following clinical features were observed: Neurological, Cardiovascular, Ventricular arrhythmias, Gastrointestinal. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - STOFF IDENT Compounds
- T3DB toxins
- ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amine
- Ester
- Ether
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Plant Toxin
|
|---|
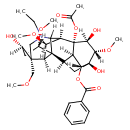
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C34H47NO11 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 645.737 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 645.315 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 302-27-2 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (1S,2R,3R,4R,5R,6S,7S,8R,9R,13R,14R,16S,17S,18R)-8-(acetyloxy)-11-ethyl-5,7,14-trihydroxy-6,16,18-trimethoxy-13-(methoxymethyl)-11-azahexacyclo[7.7.2.1²,⁵.0¹,¹⁰.0³,⁸.0¹³,¹⁷]nonadecan-4-yl benzoate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | aconitine |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@@]12C[C@@]3(O)[C@]([H])(OC(=O)C4=CC=CC=C4)[C@]1([H])[C@@](OC(C)=O)([C@@]1([H])[C@]([H])(OC)[C@@]4([H])[C@]22C1([H])N(CC)C[C@]4(COC)[C@]([H])(O)C[C@]2([H])OC)[C@@]([H])(O)[C@]3([H])OC |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C34H47NO11/c1-7-35-15-31(16-41-3)20(37)13-21(42-4)33-19-14-32(40)28(45-30(39)18-11-9-8-10-12-18)22(19)34(46-17(2)36,27(38)29(32)44-6)23(26(33)35)24(43-5)25(31)33/h8-12,19-29,37-38,40H,7,13-16H2,1-6H3/t19-,20?,21+,22-,23+,24+,25-,26?,27+,28-,29+,31+,32-,33+,34-/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | XFSBVAOIAHNAPC-BHMXGGQCSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as aconitane-type diterpenoid alkaloids. These are alkaloid diterpenoids with a structure based on the hexacyclic aconitane skeleton. These compounds have no oxygen functionality at the C7 atom. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Lipids and lipid-like molecules |
|---|
| Class | Prenol lipids |
|---|
| Sub Class | Diterpenoids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Aconitane-type diterpenoid alkaloids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Aconitane-type diterpenoid alkaloid
- Quinolidine
- Benzoate ester
- Alkaloid or derivatives
- Benzoic acid or derivatives
- Benzoyl
- Azepane
- Benzenoid
- Piperidine
- Dicarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Tertiary alcohol
- Cyclic alcohol
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Tertiary amine
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Azacycle
- Organoheterocyclic compound
- Polyol
- Ether
- Dialkyl ether
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Amine
- Alcohol
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | - Cell junction
- Cytoplasm
- Extracellular
- Microsome
- Mitochondrion
- Nerve Fiber
- Plasma Membrane
- Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
|
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | | Name | SMPDB Link | KEGG Link |
|---|
| Bacterial Chemotaxis | Not Available | Not Available | | Antiarrhythmic Drugs | Not Available | Not Available | | Rna polymerase | Not Available | map03020 | | Anticonvulsants | Not Available | Not Available | | Apoptosis | Not Available | map04210 |
|
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 204°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 0.31 mg/mL at 25°C [SEIDELL,A (1941)] |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-054k-0200069000-d5c43adf2d9e5a964f8f | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-1400095000-f69fe66a37b8742f9d88 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0a4i-3900330000-f75578a0c542f4c59099 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0006-3100039000-2583a09e7f0123c13d6e | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-056r-4200096000-b0486e36508050714f60 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-05i0-9400050000-88bb6a79c21e8a17f798 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (ingestion) (2) ; dermal (2) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Aconitine opens voltage-gated sodium channed in the heart and other tissues. (1) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Not Available |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 0.166 mg/kg (Intravenous, Mouse) (1)
LD50: 0.328 mg/kg (Intraperitoneal, Mouse) (1)
LD50: 1 mg/kg (Oral, Mouse) (1) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | 1.5 to 6 mg for an adult human. (1) |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Aconitine is a plant toxin found in species of wolfsbane (Aconitum genus). It is a neurotoxin previously used as an antipyretic and analgesic, and still has some limited application in herbal medicine. (1) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Aconitine may cause death from respiratory paralysis and cardiac arrest. (1) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of acontine poisoning include paresthesia of the whole body, starting from the extremities, anesthesia, sweating and cooling of the body, nausea, and vomiting. Sometimes there is strong pain, accompanied by cramps, or diarrhea. (1) |
|---|
| Treatment | As there is no antidote to acontine, treatment is symptomatic and may include administering atropine, strychnine or barakol. (1) |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Aconitine |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|