| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-21 20:26:39 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:42 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM002177 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Diltiazem |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Diltiazem is only found in individuals that have used or taken this drug. It is a benzothiazepine derivative with vasodilating action due to its antagonism of the actions of the calcium ion in membrane functions. It is also teratogenic. Possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, diltiazem, like verapamil, inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across both the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes. The resultant inhibition of the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells leads to dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries and improved oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue. |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - HMDB Contaminants - Urine
- STOFF IDENT Compounds
- T3DB toxins
- ToxCast & Tox21 Chemicals
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Antihypertensive Agent
- Calcium Channel Blocker
- Cardiovascular Agent
- Drug
- Ester
- Ether
- Metabolite
- Organic Compound
- Synthetic Compound
- Vasodilator Agent
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| (+)-cis-5-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2-(p-methoxyphenyl)-1,5-benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one acetate ester | ChEBI | | (2S,3S)-5-(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetate | ChEBI | | (2S-cis)-3-(Acetyloxy)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,5-benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one | ChEBI | | Acetic acid (2S,3S)-5-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-benzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl ester | ChEBI | | D-cis-Diltiazem | ChEBI | | Diltiazemum | ChEBI | | Surazem | Kegg | | (+)-cis-5-[2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl]-2,3-dihydro-3-hydroxy-2-(p-methoxyphenyl)-1,5-benzothiazepin-4(5H)-one acetic acid ester | Generator | | (2S,3S)-5-(2-(Dimethylamino)ethyl)-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydrobenzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl acetic acid | Generator | | Acetate (2S,3S)-5-(2-dimethylamino-ethyl)-2-(4-methoxy-phenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-benzo[b][1,4]thiazepin-3-yl ester | Generator | | Cardil | HMDB | | Aldizem | HMDB | | Dilren | HMDB | | Watson pharmaceuticals brand OF diltazem | HMDB | | CRD 401 | HMDB | | CRD-401 | HMDB | | Cardizem | HMDB | | Dilacor | HMDB | | Dilacor XR | HMDB | | Diltiazem hydrochloride | HMDB | | Dilzem | HMDB | | Tiazac | HMDB | | Biovail brand OF diltiazem hydrochloride | HMDB | | Diltiazem malate | HMDB |
|
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C22H26N2O4S |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 414.518 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 414.161 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 42399-41-7 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (2S,3S)-5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-3-yl acetate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | diltiazem |
|---|
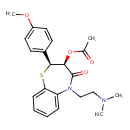
| SMILES | COC1=CC=C(C=C1)[C@@H]1SC2=CC=CC=C2N(CCN(C)C)C(=O)[C@@H]1OC(C)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C22H26N2O4S/c1-15(25)28-20-21(16-9-11-17(27-4)12-10-16)29-19-8-6-5-7-18(19)24(22(20)26)14-13-23(2)3/h5-12,20-21H,13-14H2,1-4H3/t20-,21+/m1/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | HSUGRBWQSSZJOP-RTWAWAEBSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as benzothiazepines. These are organic compounds containing a benzene fused to a thiazepine ring (a seven-membered ring with a nitrogen atom and a sulfur atom replacing two carbon atoms). |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Benzothiazepines |
|---|
| Sub Class | Not Available |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Benzothiazepines |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Benzothiazepine
- Phenoxy compound
- Aryl thioether
- Anisole
- Phenol ether
- Methoxybenzene
- Alkyl aryl ether
- Alkylarylthioether
- Monocyclic benzene moiety
- Benzenoid
- Tertiary carboxylic acid amide
- Amino acid or derivatives
- Carboxamide group
- Carboxylic acid ester
- Lactam
- Tertiary amine
- Tertiary aliphatic amine
- Monocarboxylic acid or derivatives
- Ether
- Carboxylic acid derivative
- Azacycle
- Thioether
- Organonitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Amine
- Carbonyl group
- Organic oxide
- Organooxygen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organopnictogen compound
- Aromatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aromatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | - 5-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-2-(4-methoxyphenyl)-4-oxo-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1,5-benzothiazepin-3-yl acetate (CHEBI:101278 )
|
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | White powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | 187-188°C | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | 465 mg/L (at 25°C) |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | splash10-0abc-9646000000-04d2eb286617fa811190 | Spectrum | | Predicted GC-MS | Predicted GC-MS Spectrum - GC-MS (Non-derivatized) - 70eV, Positive | Not Available | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0fb9-0900000000-96509d36ba030e8f98c8 | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0201900000-26955403b59e6618fe76 | Spectrum | | LC-MS/MS | LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-004i-0901100000-71e8128140c5e1ca0c52 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00xr-3109700000-d386c5de1a87c11cbc6f | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-7973000000-0bc5fc09ba611f5ad1fe | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-05fr-8911000000-3f9afe9e89e028c0d258 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9003300000-aa0d02f7d6ac5f92863e | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9138100000-f2b6df8ef6a8cb7aed70 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0pb9-7951000000-c5814417a1eb6c5de03b | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0001900000-8a381f5579f5f7ad42f4 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-00di-6918100000-310ffaa05668b4014162 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0229-6958000000-c55c00ddc94a8d826551 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-03di-1023900000-78474bb391c4e477c10b | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0a4i-9188100000-db8c547169ab233cd8d1 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0nov-3149000000-652c4505661022e2d0b6 | Spectrum | | MS | Mass Spectrum (Electron Ionization) | splash10-0ab9-9200000000-b1095b8fe5973d23fdd6 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Intravenous, Oral.
Diltiazem is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract but undergoes substantial hepatic first-pass effect. |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Possibly by deforming the channel, inhibiting ion-control gating mechanisms, and/or interfering with the release of calcium from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, diltiazem, like verapamil, inhibits the influx of extracellular calcium across both the myocardial and vascular smooth muscle cell membranes. The resultant inhibition of the contractile processes of the myocardial smooth muscle cells leads to dilation of the coronary and systemic arteries and improved oxygen delivery to the myocardial tissue. |
|---|
| Metabolism | Diltiazem is metabolized by and acts as an inhibitor of the CYP3A4 enzyme.
Half Life: 3.0 - 4.5 hours |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50=740mg/kg (orally in mice) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of hypertension. |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Because of its negative inotropic effect, diltiazem causes a modest decrease in heart muscle contractility and reduces myocardium oxygen consumption. Its negative chronotropic effect results in a modest lowering of heart rate, due to slowing of the sinoatrial node. It results in reduced myocardium oxygen consumption. Because of its negative dromotropic effect, conduction through the AV (atrioventricular) node is slowed, which increases the time needed for each beat. This results in reduced myocardium oxygen consumption. A reflex sympathetic response, caused by the peripheral dilation of vessels and the resulting drop in blood pressure, works to counteract the negative inotropic, chronotropic and dromotropic effects of diltiazem. Undesirable effects include hypotension, bradycardia, dizziness, and flushing. (Wikipedia) |
|---|
| Symptoms | LD50=740mg/kg (orally in mice) |
|---|
| Treatment | In the event of overdose or exaggerated response, appropriate supportive measures should be employed in addition to gastrointestinal decontamination. If bradycardia and/or high-degree AV block occurs, administer atropine (0.60 to 1.0 mg). If there is no response to vagal blockage, administer isoproterenol cautiously. Fixed high-degree AV block should be treated with cardiac pacing. In cases of cardiac failure, administer inotropic agents (isoproterenol, dopamine, or dobutamine) and diuretics. If hypotension occurs, use vasopressors (e.g. dopamine or levarterenol bitartrate). (2) |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB00343 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | HMDB0014487 |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Diltiazem |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | 35850 |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | 101278 |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 39186 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | C06958 |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Kugita, H., Inoue, H., Ikezaki, M. and Takeo, S.; U.S. Patent 3,562,257; assigned to Tanabe Seiyaku Co.,Ltd., Japan. |
|---|
| MSDS | Link |
|---|
| General References | |
|---|