| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-07-03 22:09:29 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:40 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM002066 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Tetrodotoxin |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | An aminoperhydroquinazoline poison found mainly in the liver and ovaries of fishes in the order tetraodontiformes, which are eaten. Tetrodotoxin is a potent neurotoxin that is produced by bacteria (genus Pseudoalteromonas, Pseudomonas, Vibrio) and found in certain species of Tetraodontiformes (puffer fish, porcupine fish, ocean sunfish, triggerfish), from which its name is derived. It acts on the voltage-gated sodium channels of nerve cells. (1) The toxin causes paresthesia and paralysis through interference with neuromuscular conduction. Tetrodotoxin is being investigated by Wex Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of chronic and breakthrough pain in advanced cancer patients as well as for the treatment of opioid dependence.
|
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | |
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Amide
- Amine
- Animal Toxin
- Ether
- Marine Toxin
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Sodium Channel Blocker
|
|---|
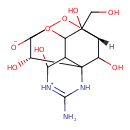
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C11H17N3O8 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 319.268 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 319.102 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 4368-28-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | (11S,13S)-3-amino-5,12,13,14-tetrahydroxy-14-(hydroxymethyl)-8,10-dioxa-2,4-diazatetracyclo[7.3.1.1⁷,¹¹.0¹,⁶]tetradec-3-en-4-ium-9-olate |
|---|
| Traditional Name | tetrodotoxin |
|---|
| SMILES | [H][C@]12OC3([O-])OC(C4C(O)[NH+]=C(N)NC4(C1O)[C@@H]3O)C2(O)CO |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C11H16N3O8/c12-8-13-6(17)2-4-9(19,1-15)5-3(16)10(2,14-8)7(18)11(20,21-4)22-5/h2-7,15-19H,1H2,(H3,12,13,14)/q-1/p+1/t2?,3?,4?,5-,6?,7-,9?,10?,11?/m0/s1 |
|---|
| InChI Key | SLBCPBUVHCASIJ-UFHSVNPDSA-O |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as tetrodotoxins. Tetrodotoxins are compounds structurally characterized by the presence of the tetrodotoxin skeleton, which is based on 5,7-(epoxymethanooxy)quinazolin-10-olate moiety. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organoheterocyclic compounds |
|---|
| Class | Diazanaphthalenes |
|---|
| Sub Class | Benzodiazines |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Tetrodotoxins |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Tetrodotoxin-skeleton
- Meta-dioxane
- Hydropyrimidine
- 1,4,5,6-tetrahydropyrimidine
- Monosaccharide
- Oxane
- Cyclic alcohol
- Tertiary alcohol
- Guanidine
- Orthocarboxylic acid derivative
- Secondary alcohol
- Carboximidamide
- Organic 1,3-dipolar compound
- Azacycle
- Propargyl-type 1,3-dipolar organic compound
- Alkanolamine
- Polyol
- Oxacycle
- Organic zwitterion
- Alcohol
- Organooxygen compound
- Organonitrogen compound
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic oxide
- Organopnictogen compound
- Organic nitrogen compound
- Organic oxygen compound
- Primary alcohol
- Alkoxide
- Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic heteropolycyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | Colorless Solid (2). |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-00di-0009000000-b7ce9130a531ed988be9 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udr-0098000000-4cc9d0d4fc807afd209b | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-000i-3091000000-da2933642dbc3ad9bc9f | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0uxr-0059000000-7c5f6a917cfd35b2ed23 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0v03-5096000000-9c701d5e323a195da9b9 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-002f-5090000000-3e75d9ff468628c782c0 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (1) ; injection (sting/bite) (1) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Tetrodotoxin binds to what is known as site 1 of the fast voltage-gated sodium channel. Site 1 is located at the extracellular pore opening of the ion channel. The binding of any molecules to this site will temporarily disable the function of the ion channel. Saxitoxin and several of the conotoxins also bind the same site. |
|---|
| Metabolism | The metabolic source of tetrodotoxin is uncertain. No algal source has been identified, and until recently tetrodotoxin was assumed to be a metabolic product of the host. However, recent reports of the production of tetrodotoxin/anhydrotetrodotoxin by several bacterial species, including strains of the family Vibrionaceae, Pseudomonas sp., and Photobacterium phosphoreum, point toward a bacterial origin of this family of toxins (3). |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | LD50: 334 ug/kg (Oral, Mouse) (1) |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | 25 mg for an adult human. (1) |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | For the treatment of chronic and breakthrough pain in advanced cancer patients as well as for the treatment of opioid dependence. Tetrodotoxin is produced by bacteria (genus Pseudoalteromonas, Pseudomonas, Vibrio) and found in certain species of Tetraodontiformes (puffer fish, porcupine fish, ocean sunfish, triggerfish), from which its name is derived. (1) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Not Available |
|---|
| Health Effects | Tetrodoxin is a potent neurotoxin and produces paralysis, which may be followed by death due to respiratory failure. (1) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of tetrodoxin poisoning typically occur within 30 minutes of exposure and include paresthesias of the lips and tongue, sialorrhea, sweating, headache, weakness, lethargy, ataxia, uncoordination, tremor, paralysis, cyanosis, aphonia, dysphagia, seizures, dyspnoea, bronchorrhea, bronchospasm, respiratory failure, coma, and hypotension. Gastroenteric symptoms are often severe and include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and abdominal pain. Cardiac arrhythmias may precede complete respiratory failure and cardiovascular collapse. (1) |
|---|
| Treatment | Treatment of tetrodoxin poisoning is supportive and symptomatic, with aggressive early airway management. In cases of ingestion gastric lavage and/or the administration of active charcoal may be performed. Alpha adrenergic agonists are recommended in addition to intravenous fluids to combat hypotension. (1) |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | DB05232 |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Tetrodotoxin |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 443368 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | C11692 |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|