| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-06-24 17:05:49 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:36 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM001737 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
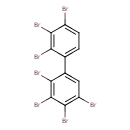
| Common Name | 2,2',3,3',4,4',5-Heptabromobiphenyl |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | 2,2',3,3',4,4',5-Heptabromobiphenyl is a polybrominated biphenyl. Polybrominated biphenyls (PBBs) are a group of 209 synthetic organic compounds with 1-10 bromine atoms attached to biphenyl. They can be used as flame retardants and may be added to the plastics used to make products like computer monitors, televisions, textiles, and plastic foams to make them difficult to burn. However, the use of PBBs is banned or restricted in most areas due to their toxicity and persistence in the environment. (3, 4) |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - IARC Carcinogens Group 2A
- T3DB toxins
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Aromatic Hydrocarbon
- Bromide Compound
- Industrial/Workplace Toxin
- Organic Compound
- Organobromide
- Polybrominated Biphenyl
- Synthetic Compound
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Formula | C12H3Br7 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 706.480 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 699.452 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 69278-60-0 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | Not Available |
|---|
| Traditional Name | Not Available |
|---|
| SMILES | BrC1=CC=C(C(Br)=C1Br)C1=CC(Br)=C(Br)C(Br)=C1Br |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/C12H3Br7/c13-6-2-1-4(8(15)10(6)17)5-3-7(14)11(18)12(19)9(5)16/h1-3H |
|---|
| InChI Key | MUVQKYHTVKKBFK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Classification | Not classified |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | Colorless to white powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | Not Available |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0000000900-b216995706a1c8799dda | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0000000900-b070446a7613446e28e8 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-0udi-0000000900-8b16a008601ecd570562 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-0002-0000009000-a77b126cb46efb8994a2 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-0002-0000009000-a77b126cb46efb8994a2 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-0002-0000019000-4c7bdfc6f2c58a3ef2d3 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (3) ; inhalation (3) ; dermal (3) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | The exact mechanism of toxicty of PBBs varies depending on the specific congener. The predominant interaction is believed to involve the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR). PBBs bind to and activate the AhR, which in turn initiates the transcriptional upregulation of a number of genes, affecting biochemical and endocrine pathways, cell cycle regulation, morphogenesis, oxidative stress response, and various other processes. This results in the numerous toxic responses characteristic of PBBs. Some of the known induced genes include the cytochrome P-450-dependent monooxygenases CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. (3) |
|---|
| Metabolism | PBBs can be absorbed via oral, inhalation, and dermal routes. Due to their lipophilic nature, PBBs, especially the highly brominated congeners, tend to accumulate in lipid-rich tissues such as the liver, adipose, skin, and breast milk. Certain PBB compounds are metabolized by the microsomal monooxygenase system catalyzed by cytochrome P-450 of the type induced by phenobarbital. The rate of metabolism may depends on the bromine substitution pattern. PBB congeners of low bromine content are transformed into hydroxylated derivatives that are predominately eliminated in the urine. Highly brominated congeners are either retained or excreted unchanged in the feces. (3) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | 2A, probably carcinogenic to humans. (2) |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | PBBs can be used as flame retardants and may be added to the plastics used to make products like computer monitors, televisions, textiles, and plastic foams to make them difficult to burn. However, the use of PBBs is banned or restricted in most areas due to their toxicity and persistence in the environment. (3, 4) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Acute Oral: 0.01 mg/kg/day (1) |
|---|
| Health Effects | PBB exposure may cause weight loss, skin disorders (such as acne), nervous and immune systems effects, and effects on the liver, kidneys, and thyroid gland. (3) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Symptoms of PBB exposure may include nausea, abdominal pain, loss of appetite, joint pain, fatigue, and weakness. (4) |
|---|
| Treatment | EYES: irrigate opened eyes for several minutes under running water.
INGESTION: do not induce vomiting. Rinse mouth with water (never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person). Seek immediate medical advice.
SKIN: should be treated immediately by rinsing the affected parts in cold running water for at least 15 minutes, followed by thorough washing with soap and water. If necessary, the person should shower and change contaminated clothing and shoes, and then must seek medical attention.
INHALATION: supply fresh air. If required provide artificial respiration. |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| Identifiers | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|