| Record Information |
|---|
| Version | 1.0 |
|---|
| Creation Date | 2009-06-19 21:58:21 UTC |
|---|
| Update Date | 2016-11-09 01:08:24 UTC |
|---|
| Accession Number | CHEM000976 |
|---|
| Identification |
|---|
| Common Name | Manganese carbonate |
|---|
| Class | Small Molecule |
|---|
| Description | Manganese carbonate is a chemical compound of manganese that occurs naturally as the mineral rhodochrosite. It is widely used as an additive to plant fertilizers to cure manganese deficient crops, in health foods, in ceramics as a glaze colorant and flux, and in concrete stains. Manganese is a naturally occurring metal with the symbol Mn and the atomic number 25. It does not occur naturally in its pure form, but is found in many types of rocks in combination with other substances such as oxygen, sulfur, or chlorine. Manganese occurs naturally in most foods and small amounts are needed to stay healthy, as manganese ions act as cofactors for a number of enzymes. (2, 3, 4) |
|---|
| Contaminant Sources | - HPV EPA Chemicals
- T3DB toxins
|
|---|
| Contaminant Type | - Food Toxin
- Inorganic Compound
- Manganese Compound
- Natural Compound
- Organic Compound
- Pollutant
|
|---|
| Chemical Structure | |
|---|
| Synonyms | | Value | Source |
|---|
| Manganese carbonic acid | Generator |
|
|---|
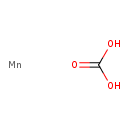
| Chemical Formula | CH2MnO3 |
|---|
| Average Molecular Mass | 116.963 g/mol |
|---|
| Monoisotopic Mass | 116.938 g/mol |
|---|
| CAS Registry Number | 598-62-9 |
|---|
| IUPAC Name | carbonic acid manganese |
|---|
| Traditional Name | carbonic acid manganese |
|---|
| SMILES | [Mn].OC(O)=O |
|---|
| InChI Identifier | InChI=1S/CH2O3.Mn/c2-1(3)4;/h(H2,2,3,4); |
|---|
| InChI Key | SDPBZSAJSUJVAT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
|---|
| Chemical Taxonomy |
|---|
| Description | belongs to the class of organic compounds known as organic carbonic acids. Organic carbonic acids are compounds comprising the carbonic acid functional group. |
|---|
| Kingdom | Organic compounds |
|---|
| Super Class | Organic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Class | Organic carbonic acids and derivatives |
|---|
| Sub Class | Organic carbonic acids |
|---|
| Direct Parent | Organic carbonic acids |
|---|
| Alternative Parents | |
|---|
| Substituents | - Carbonic acid
- Organic transition metal salt
- Organic oxygen compound
- Organic oxide
- Hydrocarbon derivative
- Organic salt
- Organooxygen compound
- Carbonyl group
- Aliphatic acyclic compound
|
|---|
| Molecular Framework | Aliphatic acyclic compounds |
|---|
| External Descriptors | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Properties |
|---|
| Status | Detected and Not Quantified |
|---|
| Origin | Exogenous |
|---|
| Cellular Locations | |
|---|
| Biofluid Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Tissue Locations | Not Available |
|---|
| Pathways | Not Available |
|---|
| Applications | Not Available |
|---|
| Biological Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Chemical Roles | Not Available |
|---|
| Physical Properties |
|---|
| State | Solid |
|---|
| Appearance | Brown powder. |
|---|
| Experimental Properties | | Property | Value |
|---|
| Melting Point | Not Available | | Boiling Point | Not Available | | Solubility | Not Available |
|
|---|
| Predicted Properties | |
|---|
| Spectra |
|---|
| Spectra | | Spectrum Type | Description | Splash Key | View |
|---|
| Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Positive | splash10-014i-0900000000-d3c9840a7de96bd4b050 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Positive | splash10-014i-0900000000-d3c9840a7de96bd4b050 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Positive | splash10-014i-0900000000-d3c9840a7de96bd4b050 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 10V, Negative | splash10-014i-0900000000-377da083c3f0ee1173b7 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 20V, Negative | splash10-014i-0900000000-377da083c3f0ee1173b7 | Spectrum | | Predicted LC-MS/MS | Predicted LC-MS/MS Spectrum - 40V, Negative | splash10-014i-0900000000-377da083c3f0ee1173b7 | Spectrum |
|
|---|
| Toxicity Profile |
|---|
| Route of Exposure | Oral (2) ; inhalation (2) |
|---|
| Mechanism of Toxicity | Manganese is a cellular toxicant that can impair transport systems, enzyme activities, and receptor functions. It primarily targets the central nervous system, particularily the globus pallidus of the basal ganglia. It is believed that the manganese ion, Mn(II), enhances the autoxidation or turnover of various intracellular catecholamines, leading to increased production of free radicals, reactive oxygen species, and other cytotoxic metabolites, along with a depletion of cellular antioxidant defense mechanisms, leading to oxidative damage and selective destruction of dopaminergic neurons. In addition to dopamine, manganese is thought to perturbations other neurotransmitters, such as GABA and glutamate. In order to produce oxidative damage, manganese must first overwhelm the antioxidant enzyme manganese superoxide dismutase. The neurotoxicity of Mn(II) has also been linked to its ability to substitute for Ca(II) under physiological conditions. It can enter mitochondria via the calcium uniporter and inhibit mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. It may also inhibit the efflux of Ca(II), which can result in a loss of mitochondrial membrane integrity. Mn(II) has been shown to inhibit mitochondrial aconitase activity to a significant level, altering amino acid metabolism and cellular iron homeostasis. (2) |
|---|
| Metabolism | Manganese is absorbed mainly via ingestion, but can also be inhaled. It binds to alpha-2-macroglobulin, albumin, or transferrin in the plasma and is distributed to the brain and all other mammalian tissues, though it tends to accumulate more in the liver, pancreas, and kidney. Manganese is capable of existing in a number of oxidation states and is believed to undergo changes in oxidation state within the body. Manganese oxidation state can influence tissue toxicokinetic behavior, and possibly toxicity. Manganese is excreted primarily in the faeces. (2) |
|---|
| Toxicity Values | Not Available |
|---|
| Lethal Dose | Not Available |
|---|
| Carcinogenicity (IARC Classification) | No indication of carcinogenicity to humans (not listed by IARC). |
|---|
| Uses/Sources | Manganese carbonate is widely used as an additive to plant fertilizers to cure manganese deficient crops, in health foods, in ceramics as a glaze colorant and flux, and in concrete stains. (4) |
|---|
| Minimum Risk Level | Chronic Inhalation: 0.0003 mg/m3 (1) |
|---|
| Health Effects | Manganese mainly affects the nervous system and may cause behavioral changes and other nervous system effects, which include movements that may become slow and clumsy. This combination of symptoms when sufficiently severe is referred to as “manganism”. (2) |
|---|
| Symptoms | Manganese mainly affects the nervous system and may cause behavioral changes and other nervous system effects, which include movements that may become slow and clumsy. This combination of symptoms when sufficiently severe is referred to as “manganism”. (2) |
|---|
| Treatment | Not Available |
|---|
| Concentrations |
|---|
| Not Available |
|---|
| External Links |
|---|
| DrugBank ID | Not Available |
|---|
| HMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| FooDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Phenol Explorer ID | Not Available |
|---|
| KNApSAcK ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BiGG ID | Not Available |
|---|
| BioCyc ID | Not Available |
|---|
| METLIN ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| Wikipedia Link | Manganese(II) carbonate |
|---|
| Chemspider ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ChEBI ID | Not Available |
|---|
| PubChem Compound ID | 24189101 |
|---|
| Kegg Compound ID | Not Available |
|---|
| YMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| ECMDB ID | Not Available |
|---|
| References |
|---|
| Synthesis Reference | Not Available |
|---|
| MSDS | Not Available |
|---|
| General References | Not Available |
|---|